(Last Updated on October 2, 2025 by Henry)
Whether you are a frequent computer user, such as an office worker, dedicated gamer, musician or painter, factory line worker, or an athlete.
Chances are, you’ve been affected by some sort of Repetitive Strain Injury at some point in your life.
A more serious or milder version of it, whether you know it or not. What to do if you’re affected by RSI? What causes this debilitating, painful condition?
What are the common symptoms & what happens if you don’t treat RSI properly early on?
How to recover quickly? What is the prognosis? Is it self-diagnosable, or should you run to a doctor immediately?
Repetitive Strain Injury is a Cumulative Trauma Disorder
First off, you should know that Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is not a single, specific medical diagnosis. It’s rather a family of conditions & medical disorders.
For example, specific types of RSI can be Tendinitis, such as Epicondylitis, including Both Medial & Lateral Epicondylitis, which we usually refer to as Tennis Elbow & Golfer’s Elbow.
Also, Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, or Bursitis, to name a few. RSI can also lead to many other closely associated conditions, such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome or even Arthritis.
What Behavioral Changes Can Indicate Repetitive Strain Injury?
Do You Experience the Following?
- Are you clumsy & keep dropping items more than you normally do?
- Are you frequently using your non-dominant hand & avoiding using the other hand that hurts occasionally?
- Are you using other limbs & body parts, such as feet, hips, elbows, or shoulders, to push the doors open?
- Are you having trouble with activities like brushing teeth, using keys, putting on jewelry, or certain clothes?
- Are you feeling weakness in your hands & changing regular shopping habits because you can carry less?
- Are you protective of your hands & you avoid using bracelets because your wrists feel tender?
- Are you frequently, subconsciously giving a self-massage to your hand?
- Are you having sympathy pain when someone else talks about their hand pain problems?
- Are you avoiding certain activities & don’t play sports that you used to enjoy?
What Symptoms Suggest You Might Have RSI?
Typical Symptoms of RSI

- Do you have chronically cold hands?
- Do you feel weakness in your fingers, hands & forearms?
- Do you have hypersensitivity & heightened awareness?
- Do you feel heaviness, like your hands are dead weight?
- Do you have a lack of coordination, & feel clumsy?
- Do you feel tingling & numbness in your fingers?
- Do you have less strength in your hands than usual?
The most common symptoms of RSI are pulsing pain & aching, weakness & tingling in arms, hands, neck, or shoulders. RSI is usually caused by cumulative traumas – Repetitive, forceful & awkward movements. It’s likely related to the overuse of muscles & tendons in both your upper & lower body.
Who Is at Greater Risk of Developing Repetitive Strain Injury?
Anyone Who’s Using Bad Posture
- Those who are using bad posture – It’s the root of evil, & the biggest risk factor in RSI cases
- Anyone who’s performing awkward movements & overall, is using bad techniques
- Those who are regularly using a computer, usually every day & more than 3 hours a day
- Anyone who does not exercise regularly is likely exposed & has a much higher risk
- Those who don’t take breaks often & are too tense, focused only on their job tasks
- Anyone who has a sedentary & unhealthy lifestyle is always at significantly greater risk
- Those who are affected with arthritis, diabetes & related serious medical conditions
- Anyone who is under continuous stress is at high risk to be affected with RSI
- Those who are overweight are vulnerable to serious medical conditions, including RSI
- Anyone who uses repetitive movements to perform their regular everyday job tasks
What Can You Do at Home to Treat & Prevent RSI?
The 5 Most Important Steps
- Modify Your Activity – If you experience pain, you need to stop that movement immediately that is causing you pain in the first place. Find proper techniques to prevent RSI as much as possible.
- Use Painkillers – Start using an ice pack, heat pack, or Over-The-Counter type of anti-inflammatory medicine to relieve pain & reduce inflammation in your muscles & tendons.
- Keep Resting – It’s mandatory to rest as much as possible to recover quickly & effectively without any further complications. Avoid cumulative injuries & trauma.
- Protect Your Arms – Keeping good posture is one of the smartest moves you can make. Depending on your condition, use elbow sleeves or wrist counter-force braces to protect your body.
- Start Physical Therapy – Start exercising as soon as possible. This can likely be a make-or-break moment if you want to make an effective change in the long run.
Follow These 5 Important Steps to Treat RSI
Is Surgery the Right Option for Repetitive Strain Injury?
Don’t Rush
This is the stage where you don’t want to rush, but you also don’t want to overlook this option too easily. Causing a dangerous situation by seeking a quick fix isn’t the most desirable solution. Avoid that if possible.
Some doctors are too hasty, rushing you to surgery, hoping to treat RSI quickly. This isn’t always the best solution; you should consider your options carefully before taking action & consult with several medical professionals.
The biggest questions that you should ask here are:
What type of RSI is it? And how severe is your case?
To have correct answers to these two questions, you want to find a qualified & competent doctor.
This is the first step in the process to conclude & confirm your RSI diagnosis.

The trickiest part is diagnosing RSI. It can be difficult in many cases, especially if one of the symptoms of the RSI condition is compression of nerves. It can cause symptoms that are deceptive in their nature.
Surgery is typically a last resort & rarely used. Recovery without surgery is possible & you want to always consider nonsurgical options first. Depending on the type of RSI, in some cases, surgery isn’t an appropriate treatment.
You should always remember that even if you have successful surgery, it’s paramount to modify your activities accordingly. Your symptoms will return if you continue the bad habits that caused the RSI condition in the first place.
What Should You Know Before Starting RSI Exercises?
What Exactly is Repetitive Strain Injury?
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) is most commonly defined in medical terms as a cumulative trauma disorder. RSI is rather a family of conditions & medical disorders than a single condition.
Repetitive Strain Injury is a very common condition that is treatable by medical professionals. Lab tests or imaging are often not required & RSI is usually self-diagnosable. Some types & cases of RSI can be difficult to diagnose.
RSI affects more than 3 million people in the US per year. The elderly people are most commonly affected. RSI usually affects age groups between 40 to 60 years but can also affect younger age groups, both men & women.
RSI is a medical condition that causes pain in nerves, muscles, tendons & ligaments due to prolonged & repetitive, as well as forceful & awkward hand movements. Poor posture, improper technique & muscle overuse combined with muscle imbalance can lead to RSI conditions.
- What is Repetitive Strain Injury? RSI is a cumulative trauma disorder, caused by overuse & repetitive motions. RSI is rather a family of disorders than a specific diagnosis – It can affect arms, wrists, hands, neck & shoulders. A form of Repetitive Strain Injury can be Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), or Tendonitis such as Tennis Elbow & Golfer’s Elbow. Also, in rarer cases, Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) & multiple related conditions.
- What are the symptoms of Repetitive Strain Injury? The common symptoms of RSI are weakness in the hands, tingling & pulsing pain. Those who are affected initially feel intermittent pain that becomes more frequent & intense over time. RSI causes acute pain, but if left untreated, it can lead to chronic pain. Pain associated with RSI can spread to muscles & joints, in the hands, wrists, shoulders, neck & also upper back.
- What causes Repetitive Strain Injury? Overuse, abuse, repetitive motion, poor posture, improper technique, awkward & forceful movements. RSI is caused by cumulative traumas rather than a single event. RSI can be associated with occupational injuries – iPod Finger, Blackberry Thumb, Mouse Arm Disease, Play-station Thumb, Rubik’s Wrist, Stylus Finger, some of the popularly referred terms.
- How to diagnose Repetitive Stress Injury? Diagnosing Repetitive Strain Injury starts with a physical examination that includes your medical history. It’s usually self-diagnosable; lab tests & imaging are often not required. Additional lab tests & imaging, such as using X-ray or MRI, can be effectively used to spot abnormalities in structure, & more importantly, to rule out other possible conditions to effectively conclude the diagnosis. If the doctor suspects an infection, blood tests can be useful to help conclude a diagnosis.
- How to treat Repetitive Strain Injury? Early-stage RSI treatment includes rest, using painkillers & modifying affected individual activities, as well as using prescribed medicine if necessary. That is usually paired up with physical therapy, & using correct postures as well as ergonomic modifications to prevent further symptoms. Also, several medical treatments are possible, such as ultrasound therapy, platelet-rich plasma & shockwave treatment. As a last resort, cortisone steroid injections are a possible solution. The most aggressive approach would be surgery if other forms of treatment are not effective enough.
- What Happens if Repetitive Strain Injury is Left Untreated? Almost always & in most cases, an acute RSI condition becomes a chronic RSI condition if left untreated. It can lead to constant pain, immobilized joints & in severe cases, completely torn, ruptured tendons. If Repetitive Strain Injury is left untreated, ultimately, some forms of RSI can even lead to Arthritis. If inflammation caused by RSI causes compression on nerves or has become infectious, it can lead to serious complications. Compressed nerves can cause numbness, tingling, and weakness & can lead to permanent nerve damage.
Diagnosing RSI properly & treating it in the early acute stage is paramount. Remember, while actively using alternative options, do not postpone seeing a medical professional.
Making a doctor’s appointment to get a precise & conclusive diagnosis can prevent serious complications. Treating a condition in its early stages is a far better solution than letting it progress to severe complications.
Where Can You Find Expert Advice on Treating RSI?
Gain Valuable Insight
How Many Different Types of RSI Exist?
Multiple Types & Related Conditions
- Tendinitis – Irritation of tissue that connects muscle to bone – Swelling, stiffness, lack of mobility & pain in tendons
- Ulnar Collateral Ligament injury (ULC) – Gamekeeper’s Thumb, or Skier’s Thumb – Repetitive trauma to the thumb
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) – Compression on ulnar nerve, causing tingling & numbness in fingers – It’s similar to CTS
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) – Compression on medial nerve in wrist – It’s a painful & progressive condition
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) – Compression of nerve or blood vessels in shoulder – Numbness & pain in neck area
- Tenosynovitis (Tendovaginitis) – DeQuervain’s Syndrome, a condition & RSI where tendon sheath becomes inflamed
- Dupuyten’s Contracture – A progressive medical condition that causes fingers to stay bent forward palm of the hand
- Diffuse RSI – It’s considered a non-specific pain syndrome, there’s pain in body but the source is difficult to locate
- Dystonia (Writers cramp) – A medical condition that causes involuntary muscle contractions, cramping & twitching
- Bursitis (Bursa Inflammation) – Fluid-filled pads that help to cushion the joints, in shoulders, knees, elbows, hips
- Ganglion Cyst – Noncancerous cysts caused by repetitive motions in wrists, fingers, shoulders, toes, ankles, knees
Learn About Different Types of Repetitive Strain Injury
What Stretches Help Relieve RSI Pain and Stiffness?
Start Light & Go From There
Resting is extra important for you, but even more important is not to be lazy & start exercising when you’ve rested enough. You don’t have to take my word for it, any competent rehabilitation doctor can tell you the same thing.
Start light, to relieve pain, meanwhile making sure that you’re not injuring yourself further. Working for more flexibility can be a smart move for you – It helps to reduce stiffness in your muscles, joints & tendons, which in addition relieves pain & helps you to heal Repetitive Strain Injury faster. Lack of exercise as well as muscle overuse are both important risk factors that you want to avoid. Stretching helps to fix & improve the overall posture, plus it relaxes overused muscles.
Working on your mobility helps your muscles to be less cramped. Doing so can be very beneficial, it likely goes a long way, & can save you from a world of pain.
It’s important to start light & accommodate your body accordingly – If you don’t want to injure yourself further, be careful. Once you’re familiar with the process, do not be afraid to add intensity. Step up your game and add more exercises. Staying positive & taking action is important. Pairing these two is what helps you to get healed up.
Always keep testing what you can do, & how you can do it. Once familiar with warm-up exercises, it’s the point where you can add additional forearm training tools, which can help you in the long run.
I recommend using simple rubber hand bands, exercise balls & wrist rollers to build well-rounded forearms & regain your functional strength as well as mobility. Strengthening weak muscles helps you greatly to prevent RSI in the future.
When Should You Exercise & When Should You Rest with RSI?
I can’t stress enough by saying that your personal diagnosis really outlines your strategies. The things you can do & what you really shouldn’t do, to recover. This is why doctor appointments are extra important for you & you shouldn’t skip any. Why? Repetitive Strain Injury can be deceptive in some particular cases, especially if nerves get compressed.
1When Should You NOT Exercise?
If you don’t know exactly what your condition is & what you’re dealing with.
For example, you might not be aware, but what if you already happen to have a nearly torn, ruptured tendon? The initial exercise can make things even worse for you & lead to further complications.
Normally, it wouldn’t happen because most of us who are currently in the world of pain would not think about exercising.
But then again, it all depends on the severity of the case & each case is unique – Not every condition is necessarily that painful, & some of the RSI conditions are more deceptive than others.
Especially those related to the compression of nerves – Patients can feel pain in one certain part of the body, but the actual source is located entirely elsewhere.
For example, the patient feels pain in the wrist & forearm, but the actual source is the compressed nerve in the shoulder. It’s already known that nerves are deceptive in that way, & if you don’t know the exact diagnosis, you might end up treating the wrong part of the body.
Using protective counter-force braces, anti-inflammatory medicine & rest are your safest, universal go-to tactics in this stage, including visiting a doctor’s office.
2When Should You Exercise?
If you know exactly what your condition is
& what you’re dealing with.
After you have consulted with your doctor & received a conclusive diagnosis from a medical professional, this is likely the safest point where you can start with physical exercises, if it’s a viable option for your current condition.
Taking out the guesswork from the picture is what gets you the best results. Everything starts with correct information.
Physical exercises are already proven to be a big part of recovery from RSI & one of the most important factors in regaining functional strength as well as increased mobility to treat Repetitive Strain Injury.
The important part is knowing that you’re in that stage & you’re ready to take action.
In this stage, meanwhile, you still keep using protective counter-force braces; it’s smart to also include physical therapy in your recovery regimen.
Starting with light stretches & later on adding exercises with specialty equipment that helps you to build & regain functional strength.
Why Is Good Posture the First Priority in RSI Recovery?
Start Changing Your Patterns…
First & foremost, start changing your routines & modify your activity that is causing Repetitive Strain Injury.
This is already a common modern hazard – Sitting in a chair, behind a computer, in an awkward position. Been there, done that. We all have, to some extent.
It really doesn’t matter how many painkillers you take, OR how many surgeries doctors are going to perform on you.
These are temporary fixes only if you don’t modify your activities.
Temporary fixes are excellent to help you “buy the time” that you can use to treat the underlying condition.
It’s recommended to use that time wisely to make some long-term changes.
The #1 priority is correcting your posture to be healthy.

Repetitive Strain Injury WILL recur eventually if you don’t stop doing what caused the condition in the first place. This is highly relevant & in many, if not most cases, a make-or-break moment for anyone who’s affected with RSI.
It’s a good idea to figure out what is breaking your body & start changing things up accordingly, a little bit at a time. It’s a smart move to start with simple, small adjustments. Make a start to change the patterns to improve your health.
How Does Posture Affect RSI and Recovery?
To Prevent Bad Stuff From Happening
What exactly is a good posture & why should you even bother with it? It’s the key to being healthier in general.
Good posture is when you are seated, or standing, in a way that you can perform your tasks, at work or home, by using minimal energy & effort.
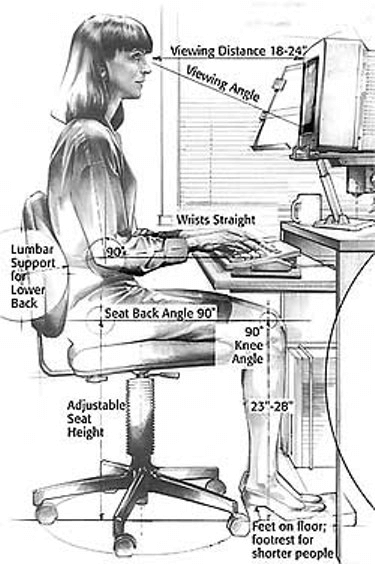
Having a good posture is associated with a relaxed, more stress-free state. It’s paired up with proper techniques & an ergonomically sound environment, which helps you to avoid being under continuous, constant strain. How to achieve better posture when seated?

- Keep your head balanced on top of your spine
- Your neck should be relaxed, without tension under the chin or back… arched in & supported by the spine
- Sit with your shoulders & arms relaxed, straight on the sides, without trying to hunch over
- Keep your upper back straight but also naturally rounded, without tension
- Have your lower back supported by a chair & slightly arched in
- Keep your pelvis & hips higher than your knees, & sit on your sitz bones, while leaning a bit forward
- Your knees should be placed directly over your feet, slightly bent & also have a small space from the chair
- Keep your feet flat on the floor for the most optimal & relaxed support
Remember, the difference between good posture & bad posture can be a very subtle one. This is a general guideline that gives you good results, but can also be hard to actualize.
Your posture can be a couple of inches off, it may look completely normal, yet it can already bring bad results for you. So, it’s important to continuously keep testing different setups, to see what you can use & how you can use it to make it effective in your case.
This is also called postural awareness & it’s a good thing if you can teach yourself to do it better & keep improving.
It’s normal, & you should be aware that our bodies are slightly different & each one is unique in its own way – It’s important to accommodate different techniques according to your own needs & options.
Why Are Ergonomic Solutions Crucial for Preventing RSI?
Prevent RSI from Reoccurring
If you’re a typical office worker, someone who has to sit behind the desk all day long, it’s highly relevant for you. Whether you’re a dedicated blogger, professional PC gamer, secretary, or someone who’s doing heavy data entry. Achieving a good posture more naturally is what you want to aim for.
Remember, it really doesn’t matter how amazing a treatment plan your doctor prescribed you unless you get your posture & ergonomics right. Otherwise, you’re just prolonging the inevitable & RSI is likely going to recur.
A couple of tiny changes, like getting better equipment, can have a significant impact on you. Swap your regular chair out for an adjustable chair to set a better height & correct angle specifically meant for you. Use ergonomic mouse & keyboard that feel comfortable, meanwhile helping to keep your good posture.
These are recommended upgrades that you should start focusing on to re-design your workspace – Especially getting an adjustable chair, it’s the biggest priority by the largest margin.
You’ll notice right away that, in most cases, adjustable chairs aren’t cheap, but you should consider them as a long-term investment. A chair determines how well you will feel after many hours of stationary work. Adjustable chair helps you
to set the best possible angle, height & and support your lower back. The right chair determines your overall posture.
How Can You Minimize the Risk of Repetitive Strain Injury?
Build Optimized Workstation
What Training Tools Help Heal RSI?
Focus On Creating Muscle Balance
The key is to focus on building more muscle balance – Having more balanced muscles is never a bad thing, whether you feel just fine or need to recover. Leverage it to get rid of symptoms of RSI & prevent them in the future.
In Repetitive Strain Injury cases, we’re frequently looking at muscle imbalance that has been caused by overuse, abuse, and forceful & awkward movements. If this problem is not addressed correctly, it usually gets only worse over time.
One could even say that muscle imbalance is one of the possible root causes of Repetitive Strain Injury. Weaker muscles are not strong enough to support the dominant ones. Dominant ones are doing all the hard work, & eventually, at some point, they are simply going to wear out.
To fix that problem, it’s important to focus on both your extensor & flexor muscles in your hand. You want to stretch both of these muscle groups regularly to reduce stiffness & also focus on extensor muscles to work your counter-movements.
This is something a vast majority of people ignore. It’s the key to healthier hands & a great way to prevent RSI.
This is often an overlooked aspect, so it gets neglected easily & it’s something most folks never do. Not because they don’t want to, it’s simply because they don’t even know how relevant it actually is. Leverage that knowledge to get better.
Why Should You Wear a Counter-Force Brace for RSI?
Use Elbow Sleeves & Wrist Braces
Using a brace is considered to be one of the safest conservative solutions & effectively applies to most RSI cases. Doctors tend to say that prevention is better than a cure. Many folks still neglect to wear a brace part. Don’t become one of those individuals. Your health is important.
If you want to get well, wearing a brace can be paramount for you. The counter-force brace is designed to prevent further injury & therefore, also help injuries heal faster. Using a counter-force brace is a scientifically proven & effective method to speed up the recovery process.
This is an excellent way to keep correct posture & protect your tendons, muscles & joints at the same time against further trauma. Your recovery should be all about avoiding the same repetitive tasks that are being performed over & over again, until the point it becomes cumulative trauma disorder.
Why Should You Revisit Doctors Even If You Know Your Condition?
RSI Can Be Tricky
How Can You Stay Consistent and Keep Recovering from RSI?
Patience Helps
- Be patient – It takes time to recover from RSI. The more patient you are, the less likely you are to injure yourself further
- Rest as much as possible to heal faster – Take breaks from activities that you can’t skip, but may cause injuries
- Do light stretching often – Keep stretching often to get your muscles more loose & flexible to reduce strain
- Keep exercising – Building more functional strength is excellent, muscles are like cushions that protect your body
- Develop YOUR pattern – Do things in your way: Work hard & modify your actions accordingly to prevent further injury
Where Can You Find Reliable References and Resources on RSI?
Thanks for Stopping By
Have Questions?
Please Leave A Comment












This is really interesting. My wife is an full-time website designer and shes always complaining about her hands feeling weak and numb. And when I touch them, they be cold as ice. I didn’t take it as anything serious, i just thought it was because shes so busy. I’ve never heard of RSI, but now i Know to take it more seriously. Great article, definitely going to send this to my wife.
Being a full-time computer worker is a high risk factor & likely leads to some form of RSI. It usually takes years to develop debilitating condition but when things are getting bad they will stay that way until it gets properly addressed.
The symptoms you describe indicate to trapped nerve. Numbness occurs when there’s too much pressure. That in turn causes weakness, since nerve is trapped it shuts down the communication between body parts.
This pretty much yells for doctors attention, I strongly recommend to get diagnosis from medical professional. Meanwhile, she could start with over the counter anti inflammatory pills if pain is there. Maybe a bit stretching & light exercises but most importantly to set up better working environment egonomics. That’s how you beat RSI, by breaking the habitual cycle that creates it in the first place.
Wow, thank you for such an in-depth explanation of such a common problem. The problem of RSI has especially grown with the usage of computer and mouse.
I’ve recently started to have uncomfortable sensations in the wrist of my right hand (the one I use for clicking on the mouse). Fortunately I am familiar with RSI so I have immediately bought a spiky rubber ball to squeeze while working on the computer. It has helped me tremendously. Also I roll the screen cleaning cloth and place it under my wrist while working on the mouse. Ok, there are more advanced things, like gelled mouse pads.
Also, are you familiar with RSI with cyclists? Sometimes I have similar uncomfortable feeling in my knees after cycling. What would be a remedy for that?
Thank you!
Knees & cycling is well in the area that RSI can affect. In this case we’re focusing on a form of sport that requires repetitive motions & a peculiar posture by its nature.
The first detail you likely want to determine is your cycling saddle height. Proper & better postures for your body. It’s important to notice if your health problem is in acute or chronic state. Both of these require quite a bit different approach to fix. Resting up & using knee sleeves for additional support can be a good universal approach. Kinesio taping is also an option if you know how to use it.
We always want to make sure if our body actually supports the activity we regularly perform. Doing different exercises for knees like squatting in gym can help to strengthen tendons around that area, stimulate bloodflow in the area & get muscles firing differenty than what they’re used. This is turn helps to balance things out.